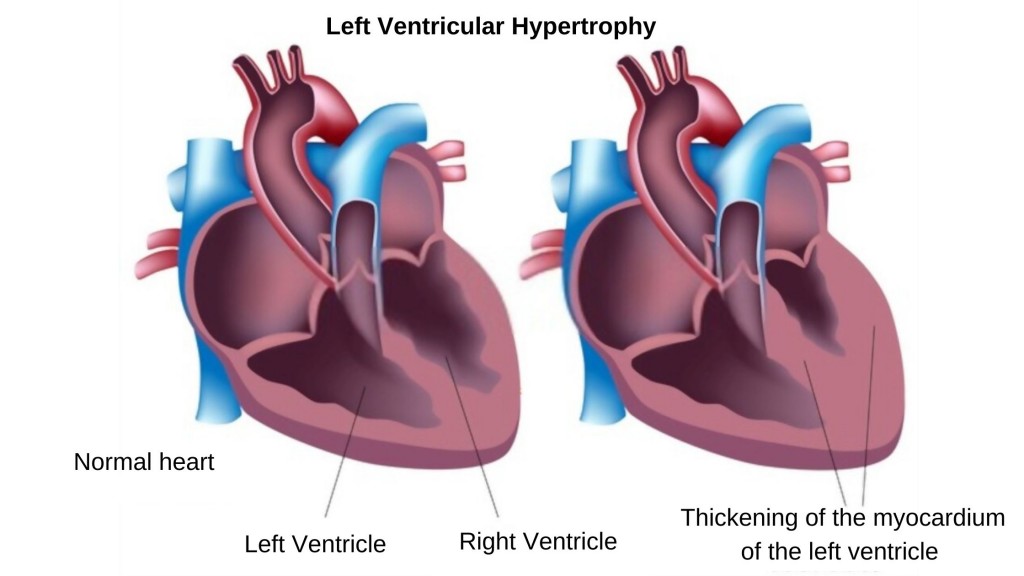

Left Ventricular Hypertrophy or LVH is a heart condition that causes mortal danger to one’s life if left untreated. LVH, as it is popularly known, is the thickening and enlargement of the heart wall in the heart’s left ventricle, a prominent blood-pumping chamber.
The thickening causes the heart muscles to lose their elasticity and become rigid. The condition adds extra pressure to the heart to fill up the chamber and pump the blood. In the long run, LVH declines the heart capacity to produce enough pressure to pump blood to the body.
The condition develops gradually, and at times goes unnoticed until it reaches critical stages. Regular heart health checks, hence, make a huge difference in keeping up with the heart-wellness.
Concentric LVH is one of the sub-types and results from the heart adapting to hypertension or other heart-related diseases. It affects men and women alike. The symptoms of concentric hypertrophy found in ECG/EKG include
Left ventricular hypertrophy occurs commonly in people with a history of high uncontrolled blood pressure. Hence, having blood pressure in control is one of the main ways to avoid LVH. LVH leads to a higher risk of congestive heart failure and irregular heart rhythms, which are life-threatening heart conditions.
Some of the general traits experienced by people with LVH are:
The most common cause of LVH is uncontrolled high blood pressure. Other causes might include
When to see a doctor?
LVH goes undetected in the early stages since the heart is trying to adjust to the changes in the best possible way without realizing it’s an abnormality. The symptoms often manifest in the later stages. Experiencing a combination of at least two of the following problems indicates that one should consult a doctor as soon as possible.
A combination of the following tests diagnoses LVH as it does not have a standalone test.
Getting blood pressure under control should ease the LVH condition. In most cases, the medications are taken to maintain regular blood pressure help prevent further enlargement of the heart and help reverse LVH. In various instances, like calcium or protein deposits found in the valves or heart, the medications might slightly differ.
The medications widen the blood vessels, lowers pressure on the heart, and decrease the pressure on the heart by improving the blood flow. The examples of these medications are:
The final option is surgery to repair the valves or the vessels, restricting the blood’s proper entry to the heart.
What can you do at home?
One of the best ways to avoid LVH is to follow a healthy lifestyle at home. Following a disciplined routine can help one avoid not only heart complications but other health problems as well.
Also, Read Seven Simple Tips to Strengthen your Heart
Disclaimer: The information included here is only for knowledge sharing purposes, and the blog is not intended to be a substitute for diagnosis, medical advice or treatment by a healthcare professional. Because of individual needs appropriate advice, the reader should consult their doctor to determine the appropriate disease depending on their situation.

 Emergency Number
Emergency Number