Before getting to know the symptoms and prevention of Hepatitis it is important to understand what is Hepatitis?
Inflammation of liver tissue, where swelling happens when tissues are injured or infected. This damage can affect how the liver functions. Located on the right side of the abdomen, under the ribs, the liver works to build protein that your body needs, and to remove toxins from the body. The liver, as a part of the immune system, therefore, plays a vital role in producing chemicals for digestion and healthy blood.
According to Wikipedia, Worldwide in 2015, Hepatitis A occurred in about 114 million people, chronic Hepatitis B affected about 343 million people, and chronic Hepatitis C about 142 million people.
Types of Hepatitis
Hepatitis can be of different types based on different causes and reasons, which are,
- Viral Hepatitis – The most common type of Hepatitis, caused because of various viruses, including viruses A, B, C, D, & E.
- Toxic Hepatitis – It is caused by poisonous chemicals, medicines, and supplements.
- Alcoholic Hepatitis – Heavy consumption of alcohol can lead to this type of infection.
- Autoimmune Hepatitis – It is a form of Hepatitis that usually attacks the liver of people with low immunity. Reasons for its cause are unknown, it can be due to environment, genetics, or lifestyle.
Hepatitis can also be classified on the basis of the Healing Period
- Acute Infection – Infection under acute cases can be cured well within 6 months
- Chronic Infection – It usually takes more than 6 months to get cured. Chronic Hepatitis is often asymptomatic in its early stages and is diagnosed by blood tests.
- Fulminant Infection – It is the rarest form of Hepatitis, which is dangerous and life-threatening. The complication occurs frequently in instances of co-infection of Hepatitis B and D at a rate of 2–20%. Hepatitis E increases the risk in pregnant women at a rate of 15–20% of cases.
Symptoms
Some of the common symptoms of Hepatitis are,
- Yellow skin and eyes
- Pale stool
- Fatigue
- Dark urine
- Loss of appetite
- Abdominal pain
- Unexplained weight loss etc.
There are certain situations where it is preferred to see a doctor,
- Recent travels to the outside country, particularly to Mexico or South America.
- Had unprotected intercourse with someone who has Hepatitis.
- Someone close to you is diagnosed with Hepatitis etc.
Causes
Different infections of Hepatitis are caused due to varied reasons.
- Hepatitis A is caused by exposure to HAV in food or water.
- Hepatitis B happens when there is contact with HBV in body fluids, such as blood, vaginal secretions, or semen.
- Hepatitis C is caused due upon contact with HCV in body fluids, such as blood, vaginal secretions, or semen.
- Hepatitis D happens due to contact with blood containing HDV.
- Hepatitis E occurs because of exposure to HEV in food or water.
Alcoholic Hepatitis is caused because of consumption of Alcohol which causes damage to the liver, which can be permanent over time and can lead to liver failure.
Inflammation can range from mild to severe in the Autoimmune system response under Hepatitis, in which the immune system attacks the liver. It is more common in women than in men.
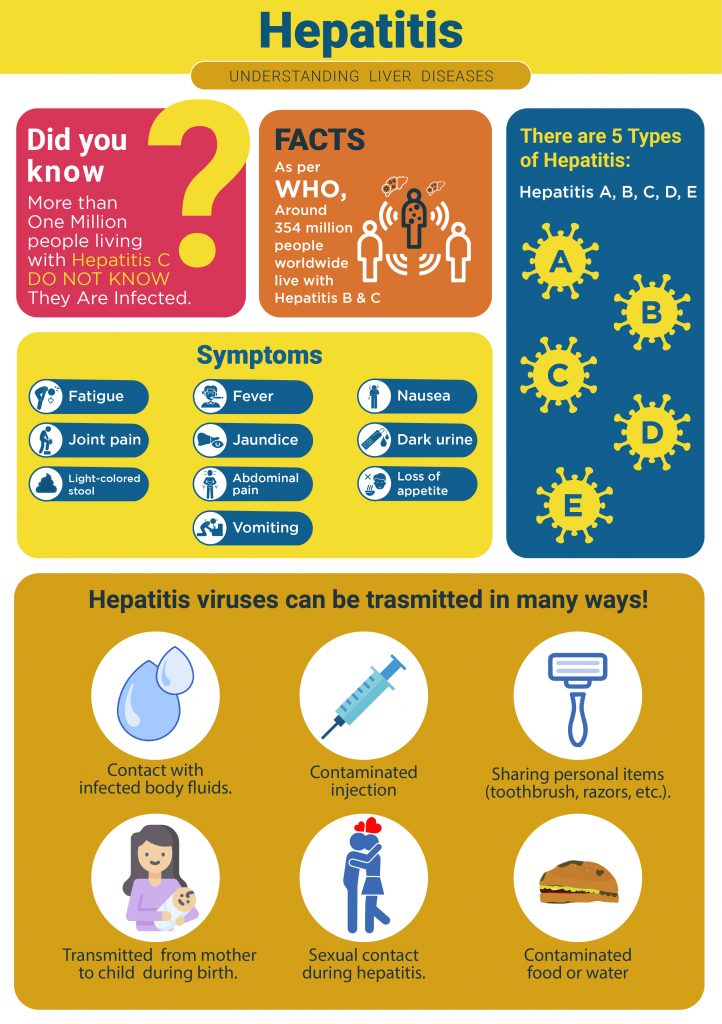
How does it spread?
Like all virus-borne infections, Hepatitis too spreads in different ways. There have been cases when the symptoms of Hepatitis surfaced, a few weeks after exposure to the virus.
Hepatitis A and E are commonly spread through food and water that may be contaminated by excreta from an infected person.
Hepatitis E is also believed to be spread through the consumption of undercooked pork, shellfish, or deer.
Hepatitis B, C, and D spread while having physical contact with the blood or body fluids of infected persons. Sharing needles for drug cravings, or having unprotected sex are some of the most common reasons for the uncontrolled transmission of the infection.
Cures and Treatment
Doctors conduct a series of tests to diagnose Hepatitis and treat it accordingly.
Along with the medical history of the patient, travel and sexual history are also pertinent to the understanding of the infection, before treatment for hepatitis. This is a classic instance when hiding facts from a primary caregiver can have adverse effects, so it is better to be upfront about one’s lifestyle and habits during medical examinations. Other tests include Liver tests, blood tests, liver biopsy, Ultrasound, Urine tests, etc.
Hepatitis A in most cases do not require treatment and cures on its own. However, in the case of heavy discomfort, bed rest is recommended.
Hepatitis B can be acute or chronic and the treatment differs for both. For the acute infection, no specific treatment is required, however, the chronic one needs antiviral medication which not only takes time but is also costly. Regular monitoring is necessary during the treatment of Virus B.
In the case of Hepatitis C, antiviral medications can treat both acute and chronic. People who develop cirrhosis or liver disease due to chronic Hepatitis C may be candidates for a liver transplant.
WHO has listed pegylated interferon alpha as a treatment for Hepatitis D, which at times has severe side effects and may not be recommended to people with cirrhosis liver damage, psychiatric conditions, and people with autoimmune diseases.
Hepatitis E often cures on its own and thus no specific medication is prescribed for the same yet.
Autoimmune Hepatitis requires medication, Corticosteroids, like prednisone or budesonide, are extremely important in the early treatment of autoimmune hepatitis. Azathioprine (Imuran), a drug that suppresses the immune system is also a part of this treatment. People may use this with or without steroids under the expert advice of a medical physician.
Severe medical conditions can also be cured with the help of surgery or a liver transplant.
Also, Read Fatty Liver Disease – An Insight
Apart from treatment, doctors advise various tips to prevent hepatitis. Here are some Do’s and Don’t s for hepatitis, which is as follows,
Do’s
• Taking Vaccines
Vaccines are available for Hepatitis A to prevent the contraction of HAV in both children and adults. Vaccines for Hepatitis B are advisable for newborns as a preventive. No current vaccine is available for Hepatitis C and E.
• Healthy and Balanced diet
• Drink boiled water or water from known resources only.
• Visit a doctor if your symptoms stay for more than 4-6 weeks.
Don’t s
• Drinking dirty or untreated local water, consumption of raw, unwashed fruits and vegetables, undercooked shellfish, pork or deer, and ice
• Sharing needles, used razors, or another person’s toothbrush.
• Unprotected sex.
Risk and Effect
While Hepatitis A and E are commonly acute and self-curable, Hepatitis B and C can be painful if untreated.
Chronic Hepatitis B & C can cause chronic liver disease (not commonly curable within 6 months), liver cancer, or cirrhosis.
Liver failure can also include,
- Kidney failure
- Bleeding
- Hepatic encephalopathy can involve fatigue, memory loss, and diminished mental abilities
- Hepatocellular carcinoma, a form of liver cancer
- High Blood Pressure
- Death
Avoiding Alcohol or certain supplements is advisable to prevent the risk of hepatitis.
Frequently asked questions about Hepatitis
- How to understand if I am infected by hepatitis?
It is not quite possible to self-diagnose hepatitis, but if a person experiences the symptoms of Hepatitis, consultation with a doctor is advisable.
2. How common is hepatitis?
Although one may hear the mention of Hepatitis often, it is quite difficult put a definite number on how prevalent the infection is, as the surveillance system to detect Hepatitis is not fully in place. It is estimated that around 257 million people are living with Hepatitis B worldwide.
3. Can a person with Hepatitis donate blood?
A person with Hepatitis is not allowed to donate blood, as it increases the chances of spreading the virus. A person with even symptoms of Hepatitis is not allowed to donate blood as a preventive measure against its contagious nature.
4. Can Hepatitis be prevented?
Yes, prevention is possible with the help of vaccination. Vaccinated people are less likely to catch Hepatitis infection. Other preventive measures mentioned in the article above can also be considered to restrict the spread of Hepatitis.
5. Who is at the higher risk of the Hepatitis bracket?
Different studies classify different age groups as high risk of Hepatitis.
Studies suggest that Hepatitis B is highest in adults aged 30-59 years as many in this group have not taken the recommended vaccinations. Infants and non-vaccinated children under the age of 19 are also potentially at risk.
Some people are more prone to the risk of Hepatitis infection due to the nature of their work or lifestyle.
- Health workers, who are in regular contact with medical instruments and needles
- People with blood transfusion and blood-related issues
- Infants born to Hepatitis infected mother
- People with multiple sexual partners.
- Injection drug users
6. How long does it take to notice the symptoms of Hepatitis?
Sometimes people with no symptoms are diagnosed with the disease and this is why it is called a silent disease. Usually, symptoms are seen within 2-6 weeks after the virus enters your body.
With Hepatitis what matters most is the remedial steps taken to diagnose and prevent the spread of the infection, not how the infection was contracted. It is important to take prevention and to receive vaccines at the right time to stay safe and healthy.
Disclaimer: The information included here is only for knowledge-sharing purposes, and the blog is not intended to be a substitute for diagnosis, medical advice, or treatment by a healthcare professional. Every individual needs advice based on diagnosis and evidence, hence the reader should consult their doctor to determine the disease and any treatment must be taken under appropriate medical guidance.

 Emergency Number
Emergency Number
does Hepatitis have an increase in its spread and how to detect it early?
Is hepatitis permanent?
Thanks this was Constructive While rules were not Supplied I appreciate the tips and checklist that was Offered Thank you 😉
I liked your content related to Is Hepatitis Curable. You have very well explained this.
Is alcoholic hepatitis curable?
Can hepatitis spread easily?
What alcoholic hepatitis is contagious?