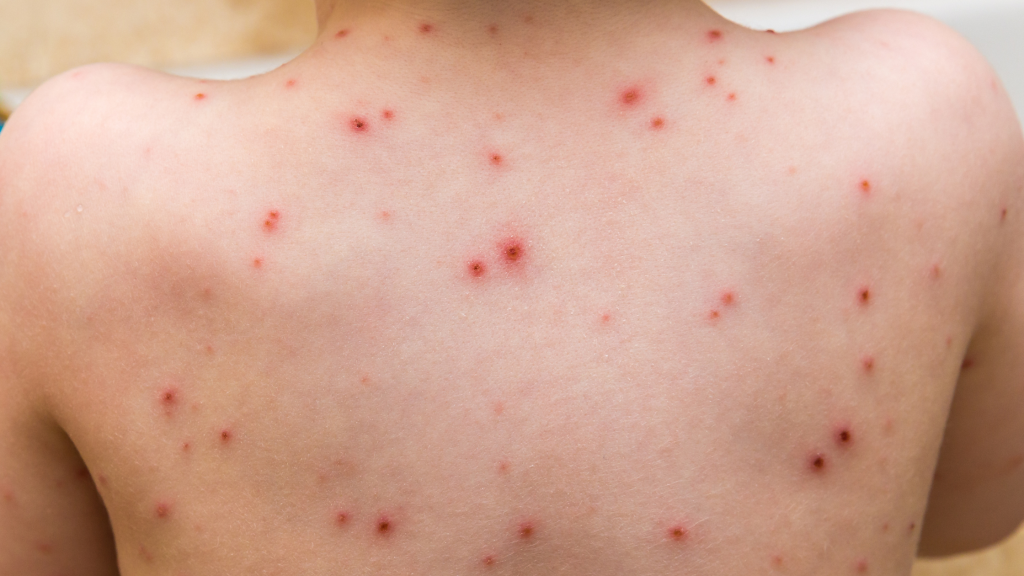



Chickenpox, also known as varicella, is an extremely contagious disease caused by the varicella-zoster virus (VZV). Symptoms of chickenpox typically include fever, fatigue, headache, and loss of appetite, followed by an itchy rash of fluid-filled blisters. There is a common myth about chicken pox that it is not serious but unfortunately, it is not true. In rare cases, there have been reports of adult persons dying because of chickenpox infection.
Make sure to distinguish monkeypox from chicken pox. Monkeypox is an orthopoxvirus whereas Chicken pox is a herpes virus. In simple terms, the main difference is that chickenpox is more contagious as compared to Monkeypox. Also, in monkeypox, there are swollen lymph nodes whereas there is no such scenario in the case of chickenpox.
The available data suggests that chickenpox is still widespread in northern parts of India like Jharkhand, and outbreaks of chickenpox continue to occur in the unvaccinated rural population.
Chickenpox is caused by the varicella-zoster virus (VZV), which is transmitted through direct contact with the rash or inhalation of airborne droplets from infected individuals. The journey of chickenpox begins with subtle signs:
Fever, fatigue, headache, and loss of appetite appear 1-3 weeks before the rash.
The hallmark feature of chickenpox is the rash. Starting on the chest, back, and face, the rash then spreads to the whole body. It develops into itchy, fluid-filled blisters that eventually scab over.
These can appear anywhere, including the face, scalp, mouth, and even genitals, adding to the discomfort.
Chickenpox progresses through distinct stages: initial flu-like symptoms, incubation period, and the emergence of a rash in waves. Understanding the stages helps manage expectations:
At the start, the symptoms are flu-like with fever and fatigue being the starting point.
The infected person may not know about the infection as the virus does not present any symptoms right after the infection. The virus silently multiplies for 10-21 days before symptoms show.
As the disease progresses the rash emerges in waves, with new spots appearing while older ones scab over. This cycle lasts 5-7 days.
Chickenpox is commonly associated with children. Therefore, it is a common myth that chicken pox only affects children. But adults can be equally infected and often the symptoms experienced by the adults are severe. The fever can turn into pneumonia and under rare circumstances can also result in the death of the person.
Babies born to mothers with no immunity or very little immunity are at higher risk of any complications. Therefore, the baby or the child may need vaccination. There is a common myth that the chicken pox vaccine can also lead to chicken pox infection due to the technicality of vaccine preparation. But vaccination is one of the best ways to protect children and also the best shield against any outbreaks.
Before going for any home remedies it is important to consult the doctor immediately. A thorough examination by a healthcare professional is essential for diseases like chicken pox. Additionally:
This blood test measures VZV immunity levels, guiding vaccination decisions.
Though caused by the same virus, these conditions have distinct presentations.
Treatment for chickenpox involves managing symptoms with over-the-counter medications, antihistamines, and antiviral medications. While chickenpox usually runs its course, several strategies can alleviate symptoms:
Over-the-counter medications can help manage fever and pain.
Antihistamines can reduce itchiness, and antiviral medications may be prescribed in specific cases.
Early intervention with antiviral medication can shorten the course of the disease.
Adults often require more aggressive treatment due to the potential for severe complications.
Supportive care and symptom management are the mainstays of varicella treatment.
Vaccination remains the most effective way to prevent chickenpox and its complications:
The varicella vaccine is safe and highly effective, protecting individuals and communities.
Unvaccinated adults or those with low immunity can benefit from vaccination.
Vaccination before pregnancy is crucial to protect both mother and baby.
While most scars fade over time, some concerns linger:
Early intervention with calamine lotion and avoiding scratching can minimize scarring.
Laser treatments or dermabrasion might be options for bothersome scars.
Chickenpox, though often considered a childhood illness, deserves a deeper understanding. By dispelling myths and embracing accurate information, we can empower ourselves and our communities to make informed decisions about prevention, diagnosis, and management. Remember, vaccination remains the cornerstone of preventing the spread of this contagious disease.
Vydehi Institute of Medical Science and Research Center is committed to providing reliable information and promoting public health awareness. We encourage you to consult with your healthcare professional for personalized advice and guidance regarding chickenpox.
Ans: The initial stages of chickenpox can manifest as non-specific symptoms like fever, headache, sore throat, or stomachache, lasting a few days with a low-grade fever. The characteristic itchy rash, often beginning on the torso and face, typically follows.
Ans: Chickenpox, formally varicella, arises from the varicella-zoster virus. Transmission occurs through direct contact with the characteristic rash or inhalation of airborne droplets expelled by infected individuals coughing or sneezing.
Ans: Chickenpox manifests in different stages over 2-4 days. Initially, red bumps appear on the skin, evolving into fluid-filled blisters with fragile walls. When these fragile walls rupture, they form open sores that eventually crust over as dry and brown scabs. The important point to be noted is that all the three stages i.e., the bumps, blisters, and the scabs, coexist simultaneously on the affected individual.

 Emergency Number
Emergency Number
This article effectively tackles common chicken pox myths and facts, clarifying misconceptions surrounding the virus and its effects. It’s crucial to distinguish between myth and reality, especially when it comes to prevention and treatment. I appreciate how it addresses fears and provides factual information to help individuals make informed decisions about their health. This is an essential read for anyone looking to better understand chicken pox. Thanks for sharing this insightful piece!