
Can the uterus shift out of its place? Can the uterus sag? The thought of it is surely daunting, however, it is true. With time, the uterus (the womb) in females can sag, or shift from its place due to overlying reasons. This condition is called Uterine Prolapse and is surprisingly a common condition in women who give birth. However, the magnitude of it might differ from woman to woman.
When a woman has undergone multiple vaginal births in her lifetime, the ligaments and muscles around the uterus can weaken. The uterus, a pear-shaped organ is located in the pelvis area. This organ comes to use during pregnancy, where it holds the developing baby. The uterus then stretches itself to accommodate the growing baby and goes back to its original size (shrinks back) post delivering the baby. When the support structure starts to erode owing to the pressure it has every time the uterus has the baby, the uterus tends to sag out of position. This is Uterine Prolapse.
Prolapses depend on the gravity of weakness of the supporting structure for the Uterus There is an Incomplete prolapse where the uterus often slips to be in between the birth canal (the vagina). This ends up creating a lump or a bulge during or after delivery. In some cases, the uterus tends to slip very far from its position, a feeling that it has come out of the vagina. This is a case of Complete prolapse.
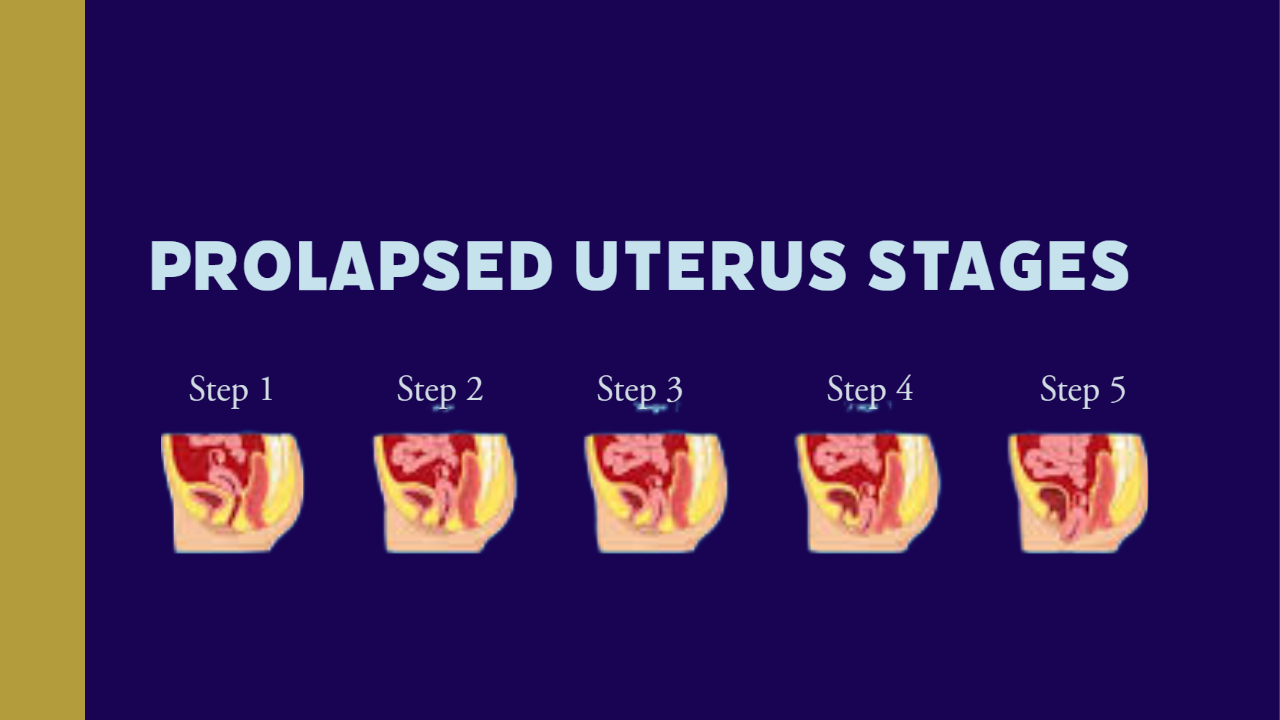
There are four stages of prolapse. The condition is graded by how severe the prolapse could get in cases where the Uterus has descended from its place.
Who is prone to prolapse?
This condition happens in women to have had multiple deliveries via the vaginal route. While a few opt for the C section, women who opt for a more natural way of childbirth are more prone to a Uterine Prolapse as there’s enormous pressure that gets created on the Uterus while pushing the baby out during delivery.
Post-menopausal women also are prone to this condition. Menopause takes place after the ovaries stop producing hormones that are responsible for the menstrual cycle (periods), after a certain age. When a woman does not have periods for the past 12 months straight, in medical terms it is assumed that the woman has hit menopause. Estrogen is one of the hormones that stop getting produced due to menopause. It is because of the absence of this hormone that prolapse can take place as Estrogen keeps the pelvic muscles and floor strong. There’s a higher chance in menopausal women to have a prolapse as the pelvic muscles tend to weaken with time without Estrogen.
An elevated BMI (Body Mass Index) is another reason for Uterine Prolapse. People who are above the prescribed BMI are said to be obese and obesity is also a reason for women to get a uterine prolapse. In obese women, there is an increase in intra-abdominal pressure that causes the pelvic floor muscles to weaken.
Women who indulge in regular smoking are also at a higher risk of a Uterine Prolapse. Regular smoking can cause chronic coughing and coughing constantly can damage the muscles of the pelvic floor. When these muscles are damaged, the strength left in these muscles to hold the uterus also weakens. Research has also shown that a smoking-induced activation of vaginal macrophage elastase can also act as a contributor to Uterine Prolapse.
When the uterine prolapse is mild, one might not experience any symptoms. However, when the uterus further slips out from its position and places itself at places that put pressure on other pelvic organs, is when it becomes a problem. A few symptoms to watch out for are –
An important thing to know in case of Uterine Prolapse is that there could be abnormal or irregular vaginal bleeding. It happens so, because the uterus shifts from its place, thereby increasing the chances of wounding the insides of the pelvic area. As the uterus places itself somewhere else abnormally, the bulge that gets created could also cause bleeding in some cases. All in all, while it is not a common symptom, depending on how severe the prolapse is, bleeding could be there. One must seek immediate medical intervention in case of abnormal bleeding, along with other symptoms mentioned above.
Uterine Prolapse if left untreated can turn severe, where the uterus shifts far from its place and places itself near the vagina. It can also appear to be a protruding tissue from the vagina, and that can contribute to urine with blood. In case, the uterus places itself near our bladder, there could be painful urine with little or no blood, again, depending upon the gravity of the prolapse. An untreated prolapse can interfere with our bowel and bladder movements, hence diagnosis and treatment are a must to avoid leading a painful life.
How can one treat Uterine Prolapse naturally (or non surgically)?
It is essential to consult a medical professional even when there are minutest symptoms. Uterine prolapse is diagnosed by the healthcare provider by performing a pelvic examination to see if the uterus has indeed moved from its position or not. The diagnosis is done by inserting a speculum (an instrument that lets the doctor see the inside of a vagina) to examine the uterus by feeling if there are bulges caused when the uterus has been displaced and has dropped down into the vaginal canal.
Once the prolapse is confirmed, the health care provider may provide a list of remedies to cure the prolapse. There are surgical and non-surgical options for the same.
The health care provider will initially suggest natural treatments that one can do on their own with minimal medical supervision like –
Are there Surgeries for Uterine Prolapse?
Surgery is not recommended unless necessary. It is recommended to consult a doctor before trying any of these remedies, or by understanding the repercussions of surgery. Surgery is usually suggested in cases where the uterine prolapse is moderate to severe. There is Laparoscopic Surgery where instruments are inserted through the navel and the uterus is pulled back to its original position, reattached to its ligaments.
There is also a surgical procedure called the Hysterectomy where the Uterus is surgically removed. This is done by making an incision (cut) in the vagina or through the abdomen. This is major surgery and connotes pregnancy, no longer to be possible as the uterus wouldn’t be a part of the body to support the developing baby.
Also Read: Carpal Syndrome in Pregnancy
The surgery may or may not have a complication, depending on the degree of uterine prolapse and whether the stage it was at, was fatal. However, surgery could be riskier if one has heart disease, has breathing problems, is a smoker, is obese, or has diabetes. There are chances that the prolapse can happen again hence, surgeries usually are done after the women are done having children.
Not treating the prolapse or not having a timely detection of the prolapse can deter other bodily functions as well. It is absolutely important to prevent these prolapses if possible and they can be achieved by –
They say prevention is better than cure, hence in the case of Uterine Prolapse, one has to watch out for alarming symptoms. If one feels that they might have this condition owing to a recent pregnancy or an injury in the pelvis area, immediate medical attention is a must. Building good lifestyle habits can keep you away from this daunting condition and after-effects.
Disclaimer: The information included here is only for knowledge sharing purposes, and the blog is not intended to be a substitute for diagnosis, medical advice, or treatment by a healthcare professional. Because individual needs appropriate advice, the reader should consult their doctor to determine the appropriate disease depending on their situation.

 Emergency Number
Emergency Number